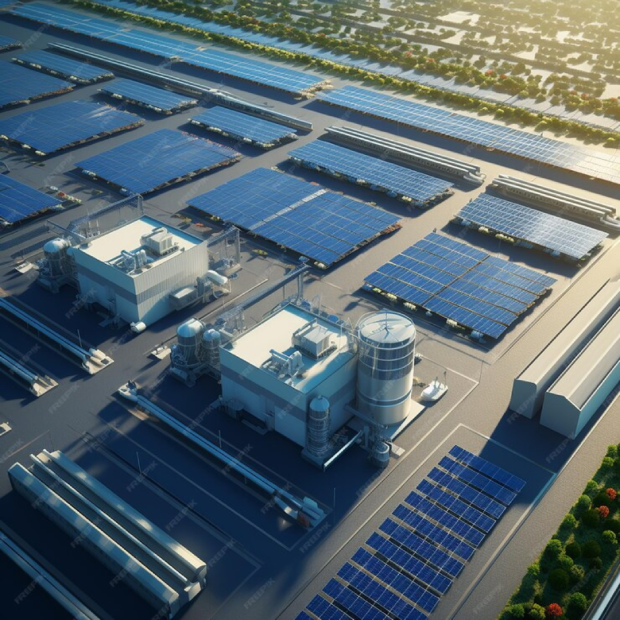

The most common form of ESS, including lithium-ion, lead-acid, and flow batteries. They offer flexibility and can be deployed for various applications, from residential use to grid-scale projects.
This technology stores energy in the form of heat, which can be used for heating or converted back into electricity. It’s particularly effective in conjunction with solar thermal systems.
Maintains reliable electricity supply, reducing blackout risks effectively.
Stores excess renewable energy for consistent, reliable usage.
Lowers energy costs by optimizing consumption during off-peak times.
Ensures power availability during outages for homes and businesses.
Reduces fossil fuel reliance, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions significantly.

Quickly adapts to changing energy demands, optimizing grid performance.